Ryton Excellent high temperature resistance – Some PPS compounds can operate continuously to 450 °F ; Flammability (UL 94) V-O/5VA – Very low smoke emission ; Excellent chemical, radiation and hydrolysis resistance ; Very resistant to creep, deformation under load and compression set ; Excellent tribological properties at elevated temperatures ; Very good electrical properties in certain formulations.
PTFE is a crystalline polymer with a melting point of about 621° F (327° C). Density is 2.13 to 2.19 gm/cc. PTFE has exceptional resistance to chemicals. Its dielectric constant (2.1) and loss factor are low and stable across wide temperature and frequency range. PTFE has useful mechanical properties from cryogenic temperatures at 500° F (280° C) continuous service temperatures. Its coefficient of friction is lower than almost any other material. It also has a high oxygen level.
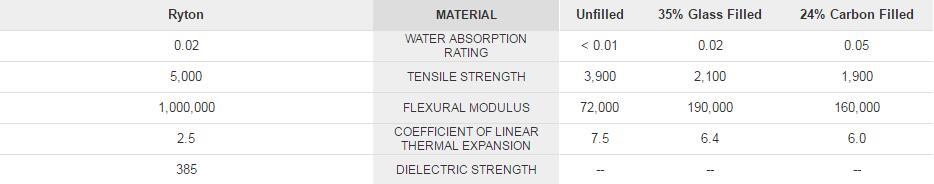
Comparison of Ryton and Polymer PTFE/FEP Property Values:
Material Applications:
Ryton:Pumps;Bearings;Pistons;Gears.Polymer PTFE/FEP:Cabling solutions;Non lubricated bearings;O-rings;Seals;Capacitors;Semiconductor manufacturing;High temperature electrical parts;Gaskets;Valve components.
Material Properties:
Ryton:Excellent chemical resistance;Almost no moisture absorption;Machines to tight tolerances;Inert to steam, strong bases, fuels and acids;Very low coefficient of linear thermal expansion;Inherently flame retardant;Dimensional stability;High mechanical strength;High strength-to-weight ratio.
Polymer PTFE/FEP:Excellent dielectric properties;Inertness to most chemicals;High heat and chemical resistance;Very low coeffiecient of friction;Excellent radiation resistance;Zero moisture absorption;Relatively insensitive to power frequency;Machinability.
Post time: Jan-14-2017

